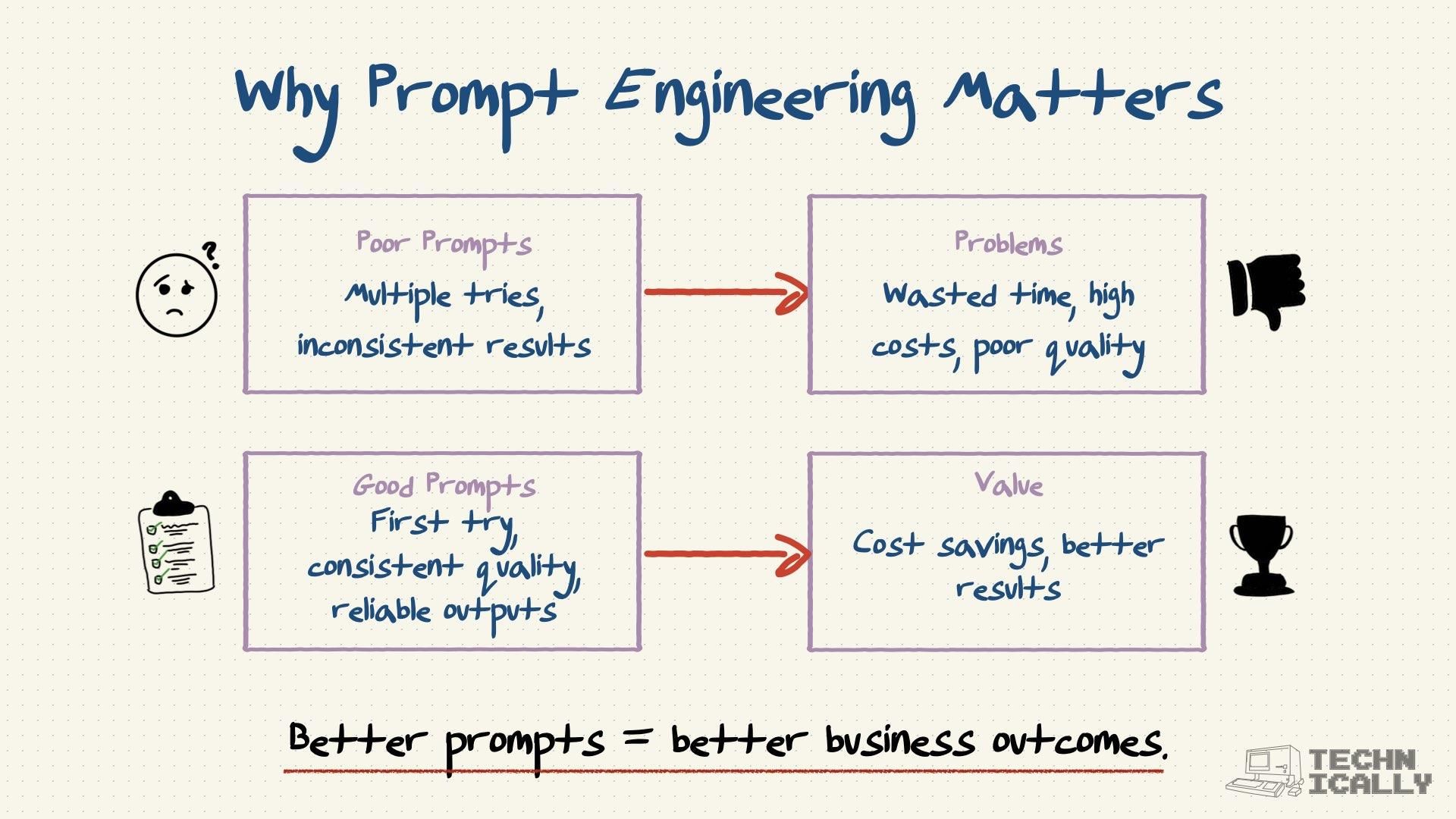
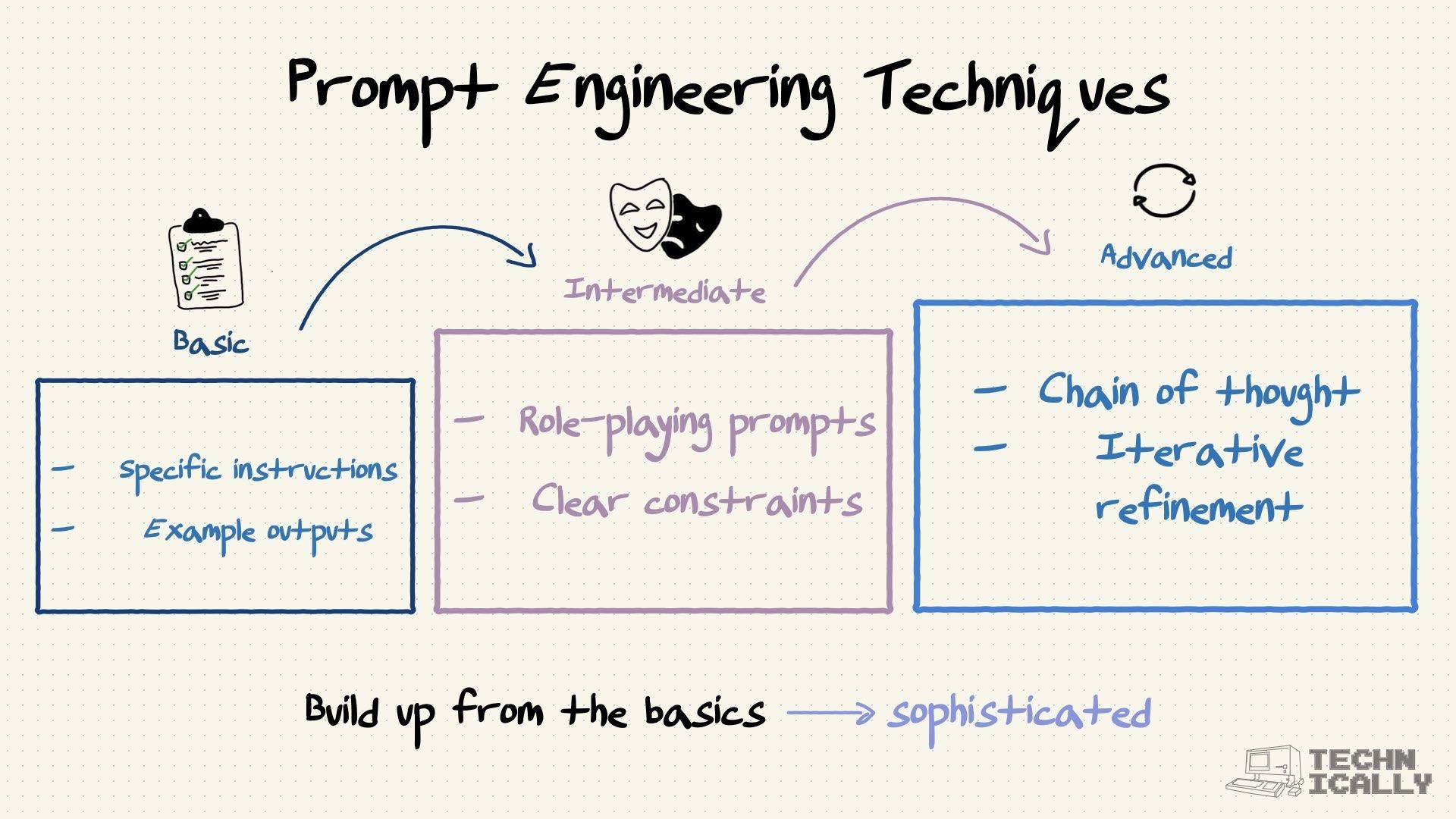
What are prompt engineering techniques?
Beyond just best practice for writing good prompts, the field has developed several reliable techniques that work across different AI models. These are more on the “engineering” side of prompt engineering.
Few-Shot Prompting
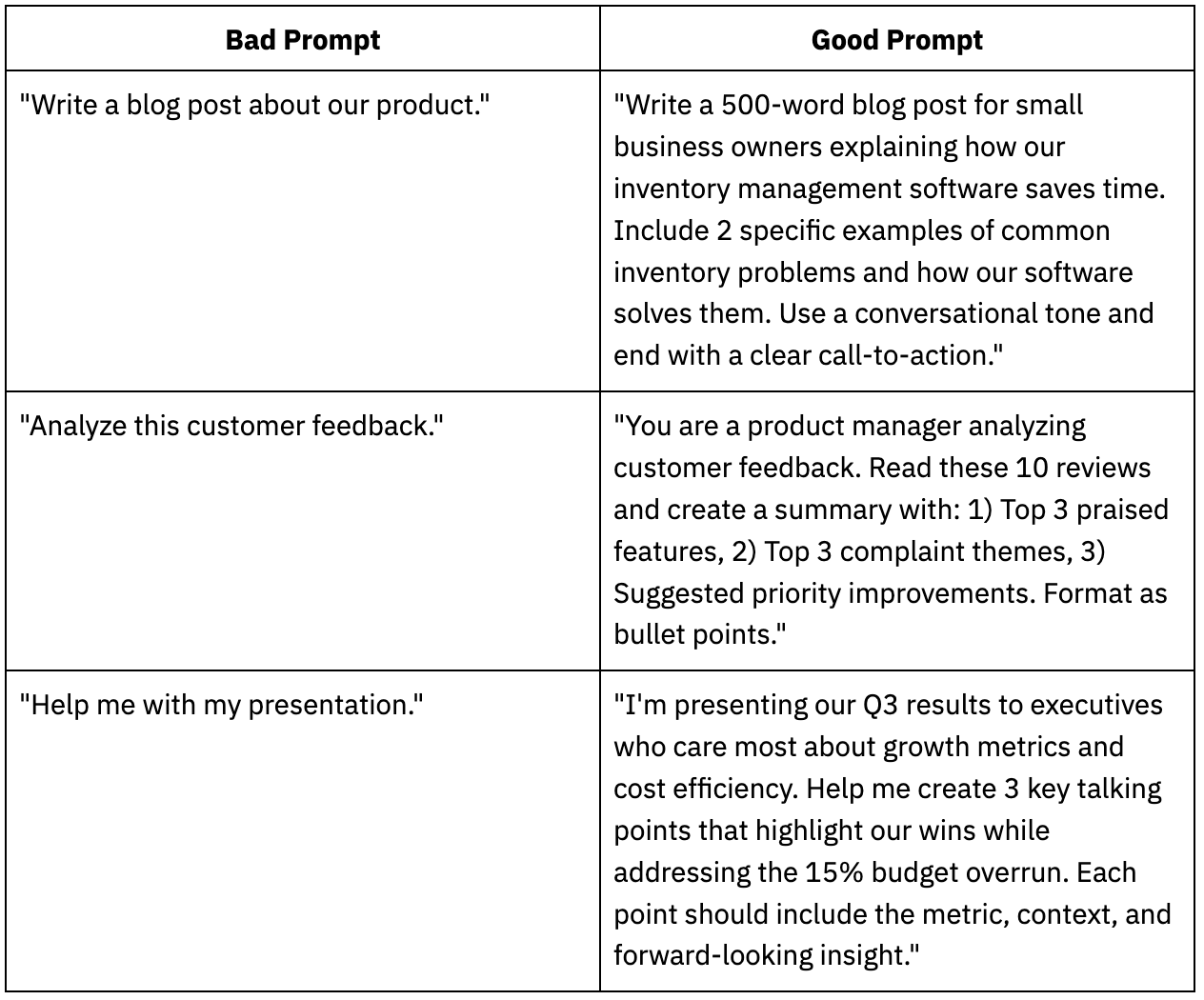
Give the AI a few examples of what you want before asking it to generate something new. Instead of just saying "write me some email subject lines," you'd show it what good ones look like first:
"Here are three email subject lines that worked well for us:
- 'Your Q3 report is ready—3 key findings inside'
- 'Quick question about tomorrow's demo'
- 'Following up: Next steps for the Henderson account'
Now write 5 more subject lines in the same style for our new product launch email."
The examples teach the model your specific style and format without you having to describe it in abstract terms.
Chain of Thought
Ask the AI to work through problems step by step rather than jumping straight to an answer. This is especially useful for anything involving logic, math, or complex reasoning.
Instead of: "What's 15% of our $847,293 annual budget?"
Try: "Let's calculate 15% of our $847,293 annual budget. Work through this step by step, showing your reasoning."
The phrase "step by step" or "let's think through this" often produces more accurate results because it forces the model to show its work rather than pattern-matching to an answer.
Constraints and Boundaries
Set clear limits on length, format, or information sources. This prevents the AI from rambling or hallucinating.
"Summarize this product spec in exactly 3 bullet points, each under 15 words" or "Only use information from the attached document—don't add anything from your training data."
Specific constraints force the model to prioritize and stay focused rather than generating everything it associates with a topic.