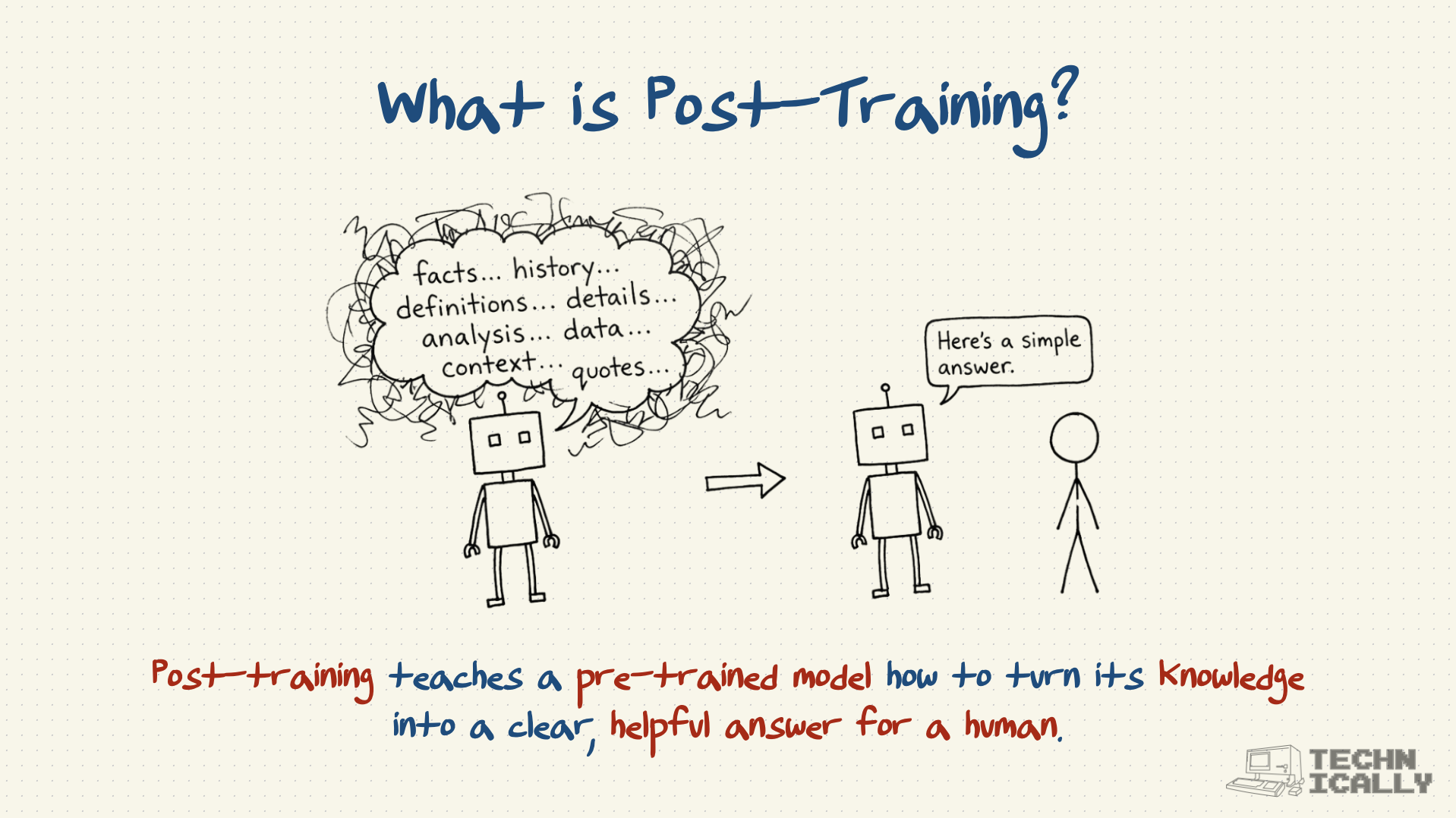
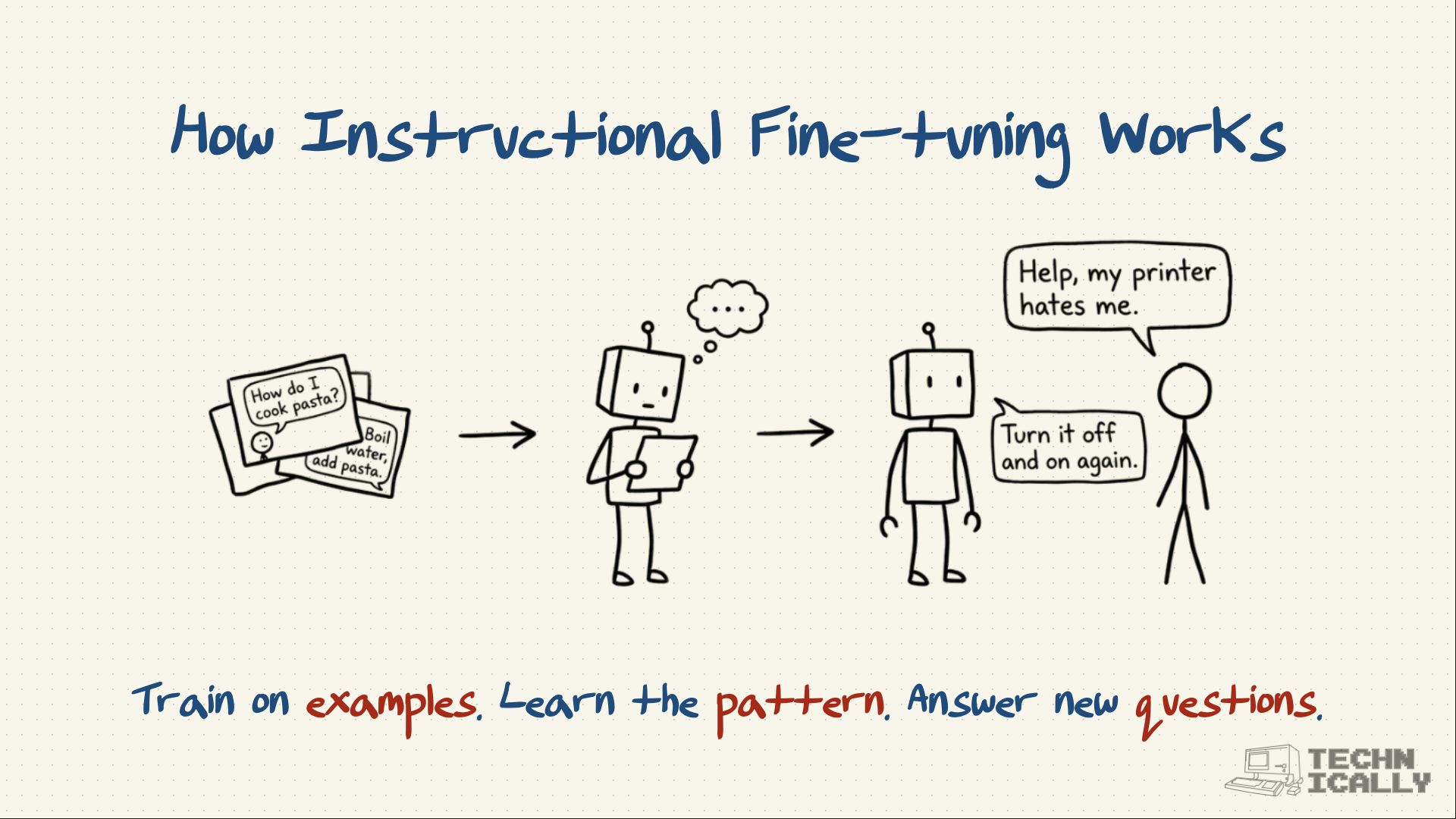
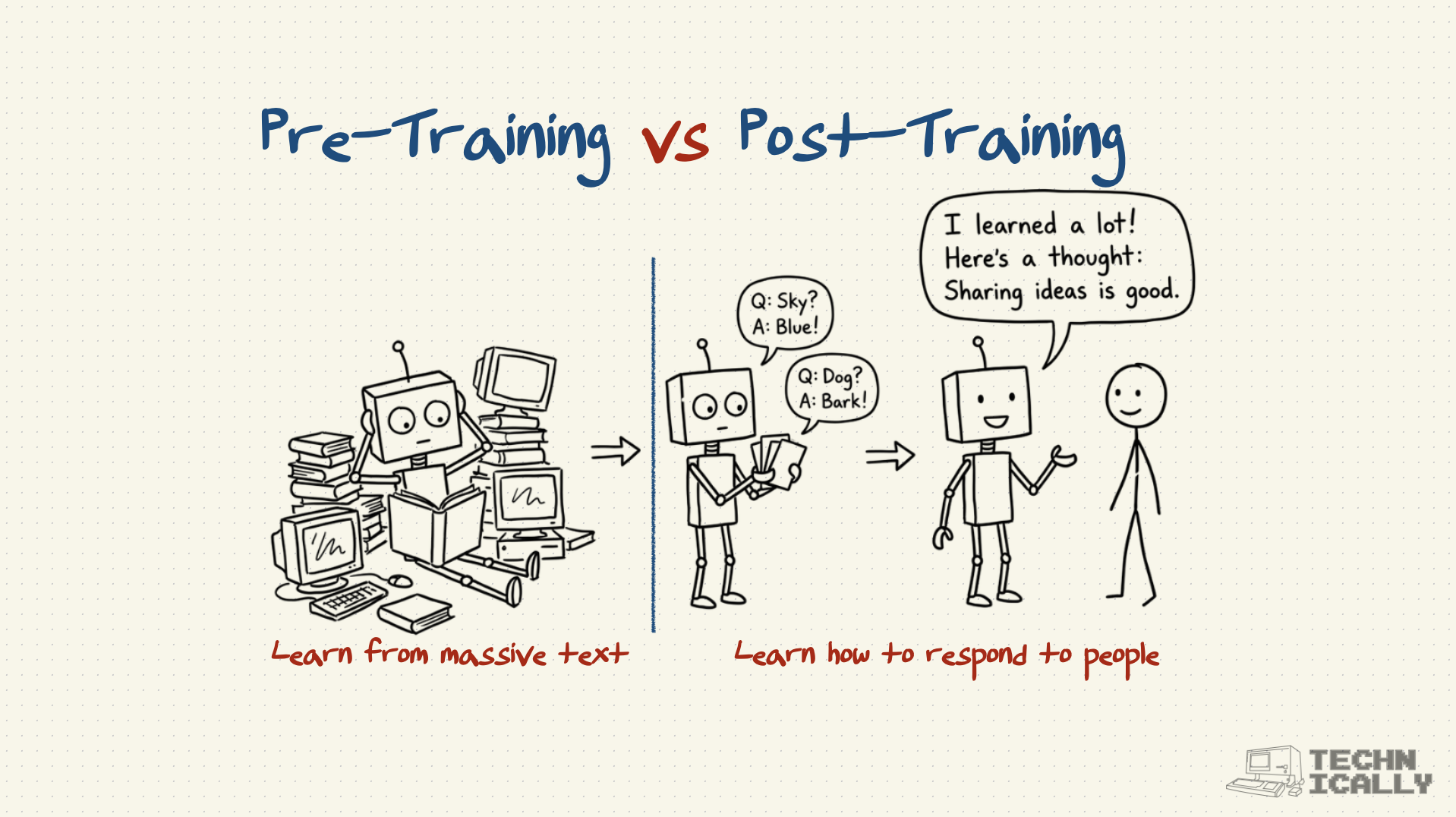
What's the difference between pre-training and post-training?
The difference is like the difference between cramming for a test and learning how to teach:
Pre-training: "Read everything on the internet and memorize it"
- Creates vast knowledge but poor communication skills
- Model knows facts but doesn't know how to be helpful
- Responses are technically accurate but often useless
Post-training: "Learn how to package that knowledge helpfully"
- Teaches conversational skills and social awareness
- Model learns what humans actually want to hear
- Responses become concise, relevant, and genuinely useful
Here's a concrete example:
Question: "I'm feeling stressed about work"
Pre-trained model: "Stress is a psychological and physiological response to perceived threats or challenges, historically evolutionary advantageous for survival but in modern contexts often maladaptive, characterized by elevated cortisol levels and activation of the sympathetic nervous system..."
Post-trained model: "I'm sorry to hear you're feeling stressed. Here are a few quick things that might help: take some deep breaths, step away from your desk for a few minutes, or try writing down what's bothering you. Would you like to talk about what's causing the stress?"
Same knowledge base, completely different approach to being helpful.