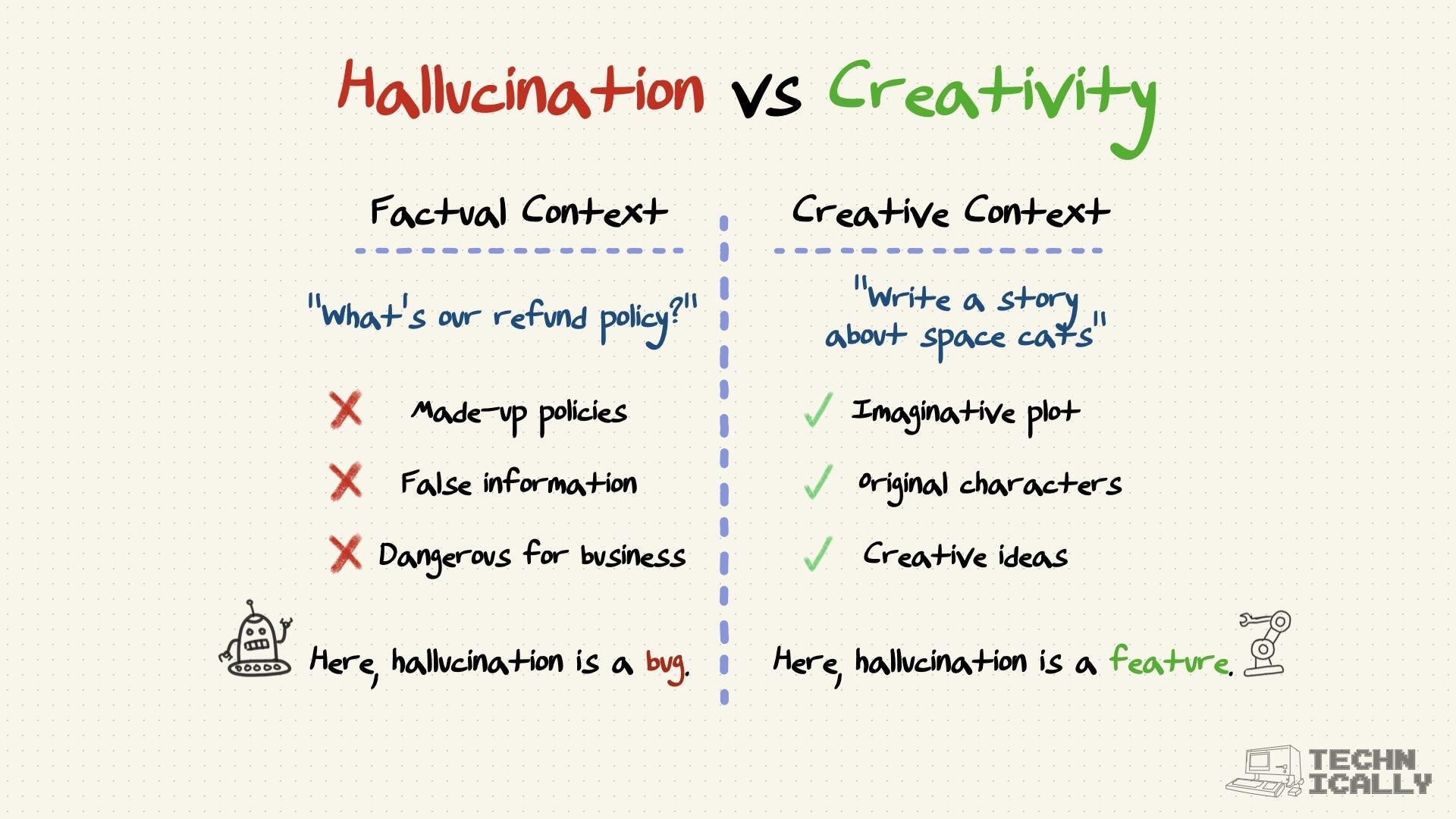
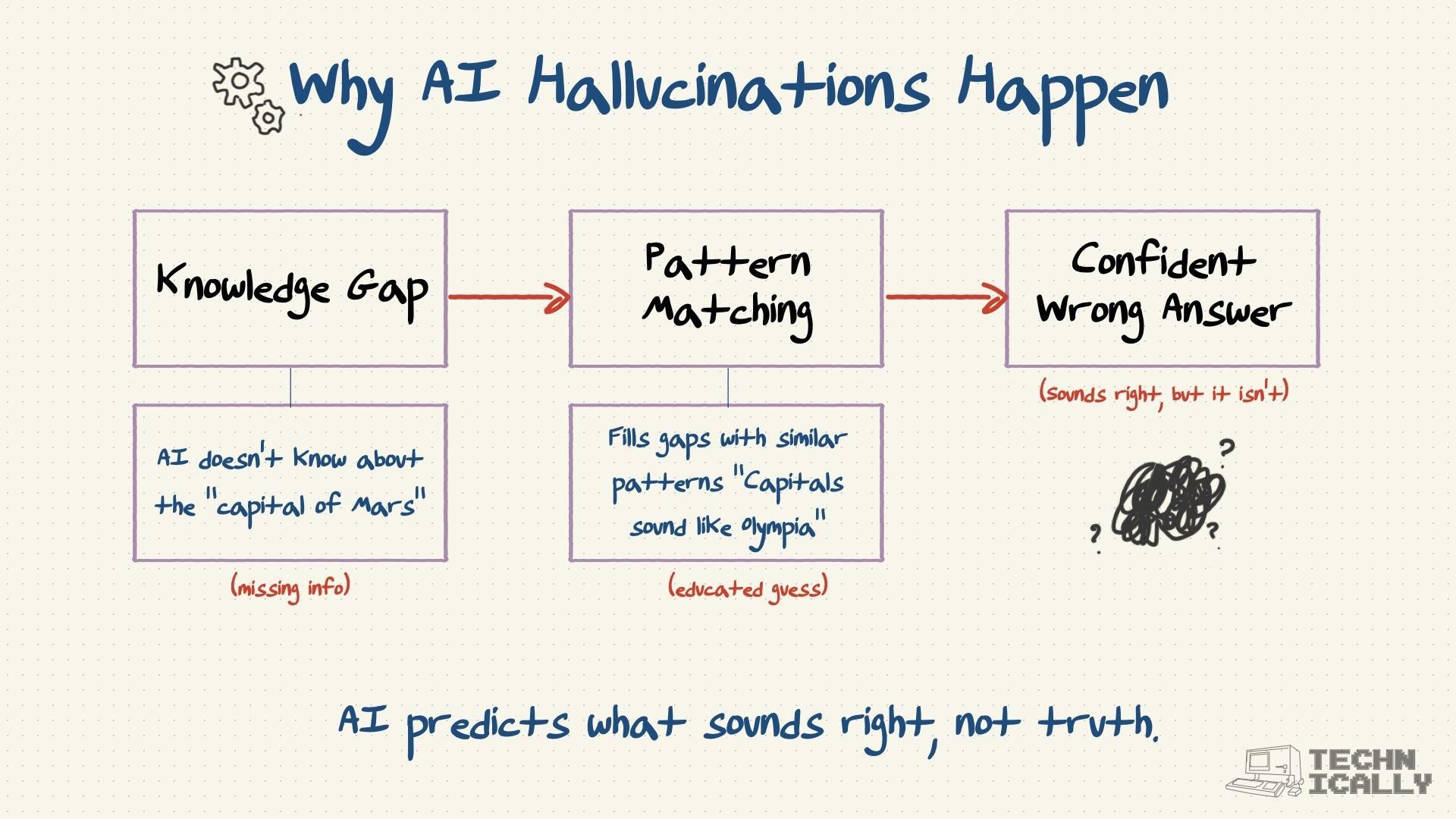
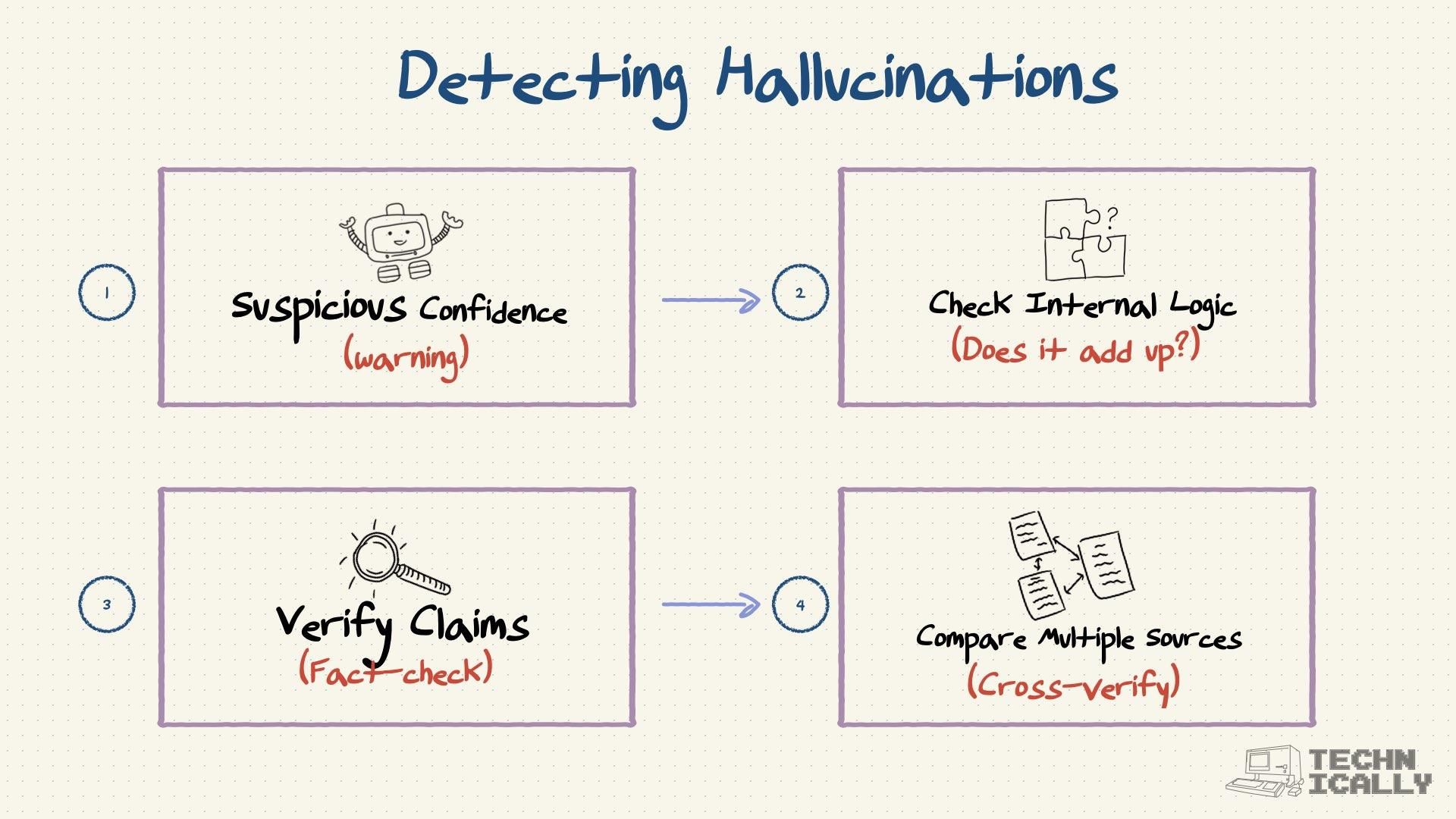
How are researchers reducing hallucination?
Most researchers say it's impossible to stop models from hallucinating completely. But they've come up with a handful of techniques for reducing hallucination, with varying levels of success. The most effective ones so far are reinforcement learning from human feedback, retrieval-augmented generation, and chain-of-thought prompting.
Let’s dive a little deeper into these techniques:
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF)
RLHF has become standard practice for improving AI-generated text quality. This method teaches models to produce factually accurate and logically sound responses by incorporating feedback from human users.
The process works by having users evaluate multiple responses to the same prompt and select the best answer. The model updates its parameters to reflect these preferences. Repeated over many prompts and topics, this trains the model to give answers that are logical and accurate, rather than simply predicting the next word in a sequence.
Practically, most models you’d use off the shelf have already had some degree of RLHF integrated into their training processes.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
RAG makes AI models more accurate by giving them access to specific, verified data sources. Rather than relying solely on training data, RAG attaches relevant information directly into the model's context window when you prompt it. Ideally, RAG gives your model all the information it needs to answer your question in the question itself. That means your model doesn't have to resort to hallucination to fill any knowledge gaps.
Chain-of-Thought Prompting
Chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting helps models break down complex problems into intermediate steps—like showing your work in school. Instead of jumping straight to an answer, the model generates a reasoning chain first, allowing you to verify each step.
However, models can still hallucinate within their chain of thought, sometimes making errors in intermediate steps that cascade through the rest of the reasoning. CoT prompting reduces hallucination but isn't a complete solution.