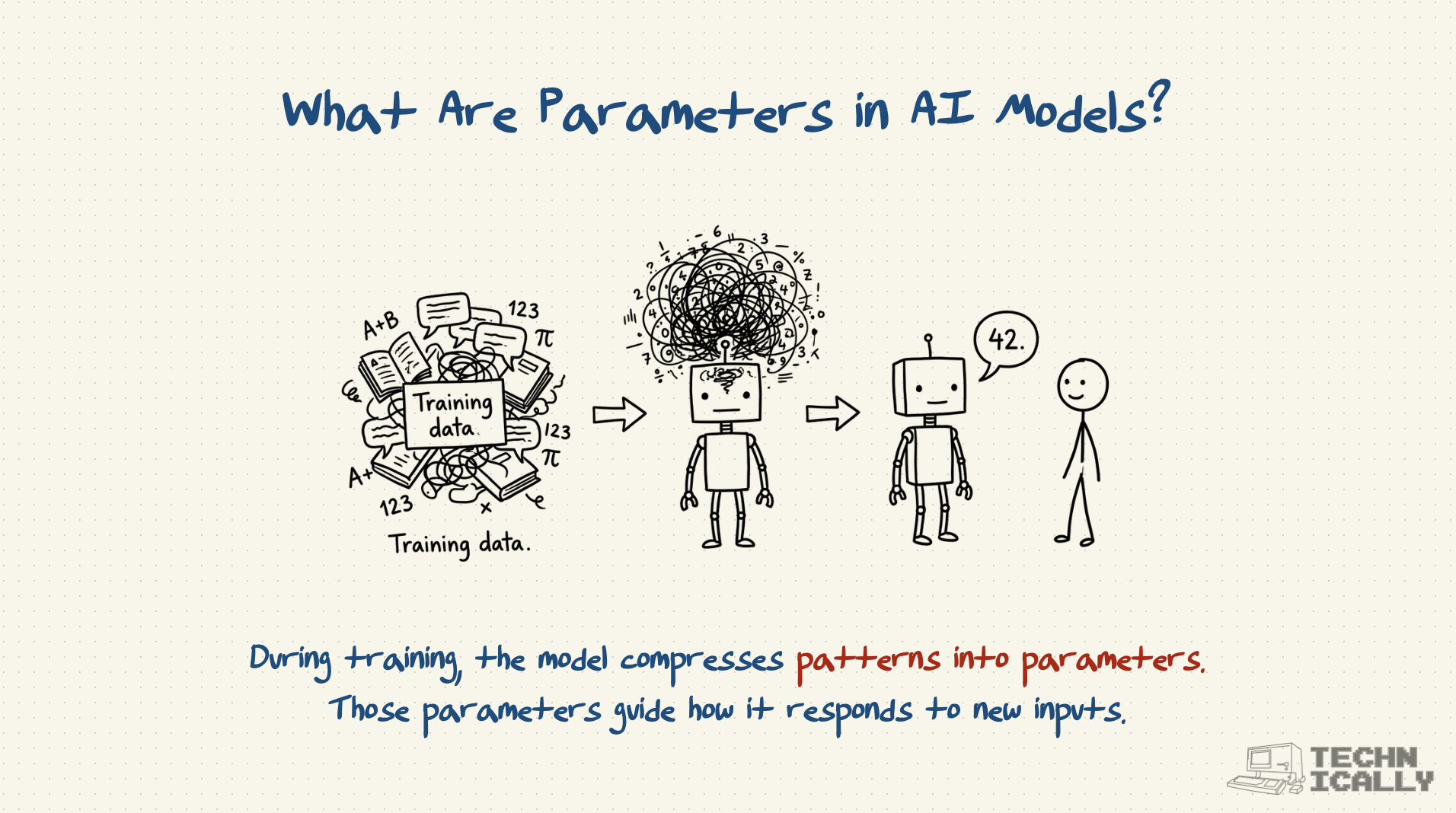
Frequently Asked Questions About Parameters
What's the difference between parameters and hyperparameters?
- Parameters: Learned during training (the model's "knowledge")
- Hyperparameters: Set before training (learning rate, model size, training duration)
Think parameters as what the student learns, hyperparameters as how you teach them.
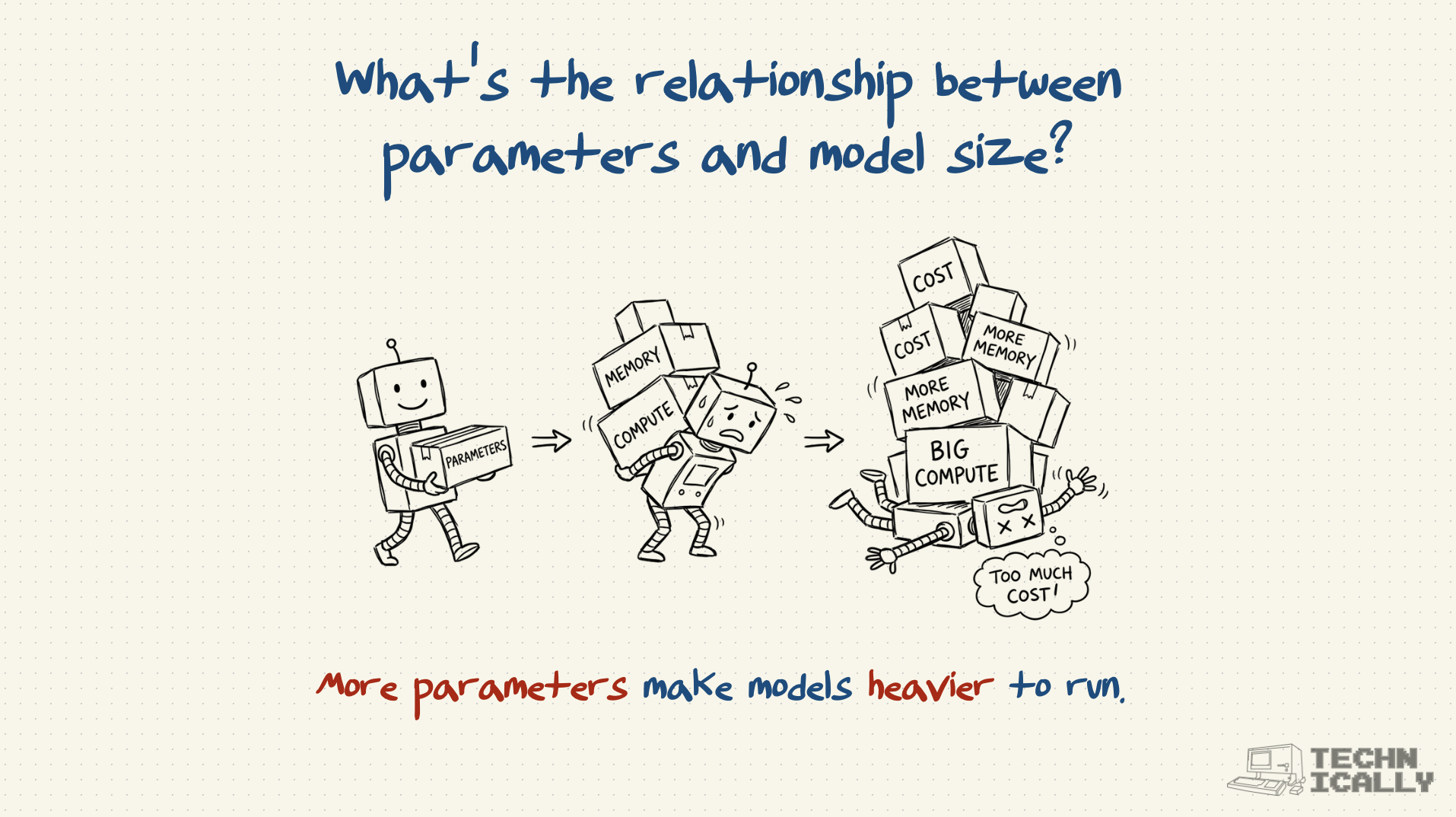
How much memory do parameters require?
Roughly 2-4 bytes per parameter for storage, plus additional memory for processing. A 7B parameter model needs about 14-28GB just to load, before doing any calculations.
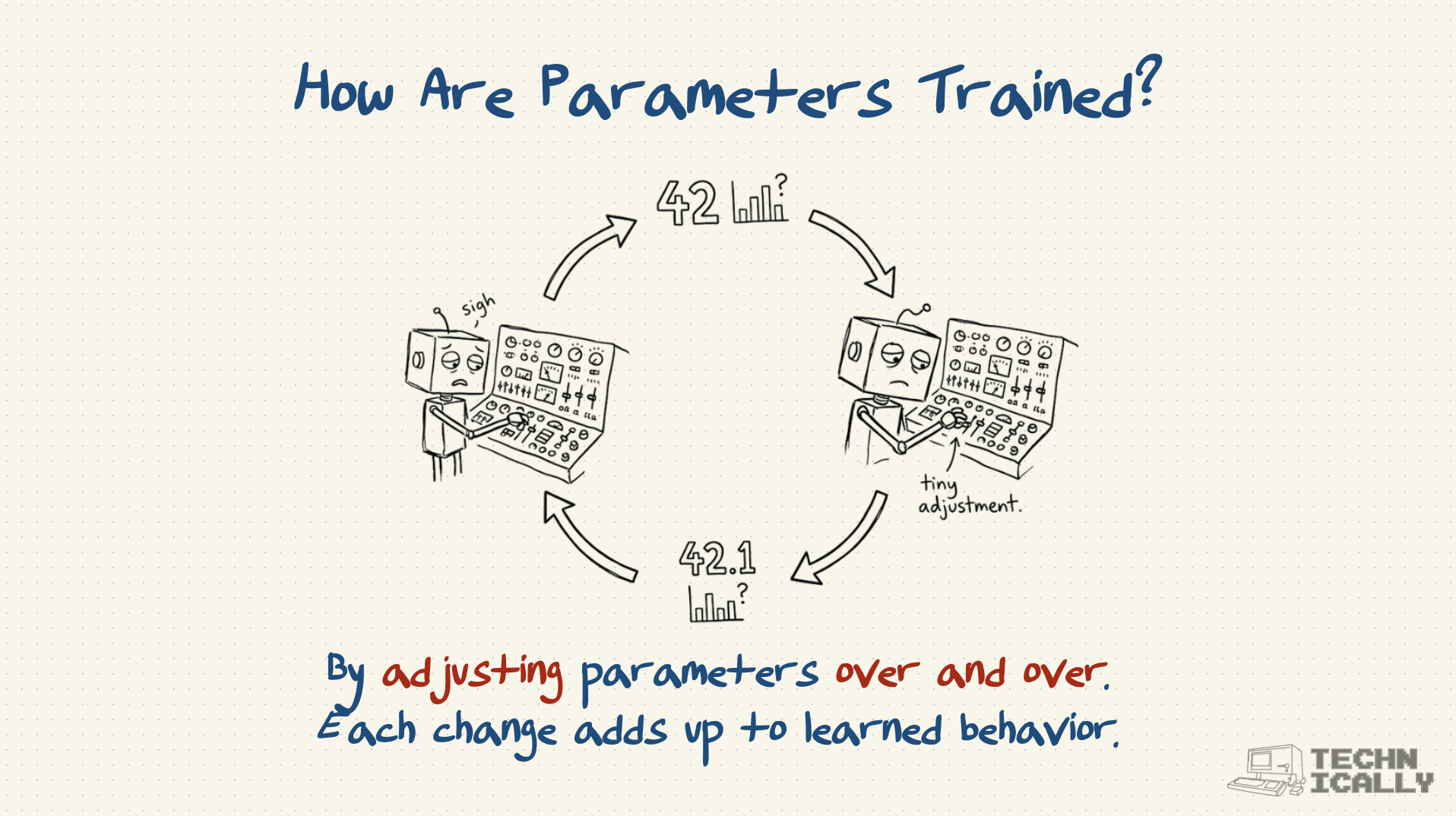
Can you modify parameters after training?
Yes, through techniques like fine-tuning (adjusting parameters for new tasks) or pruning (removing less important parameters). But major changes usually require retraining.
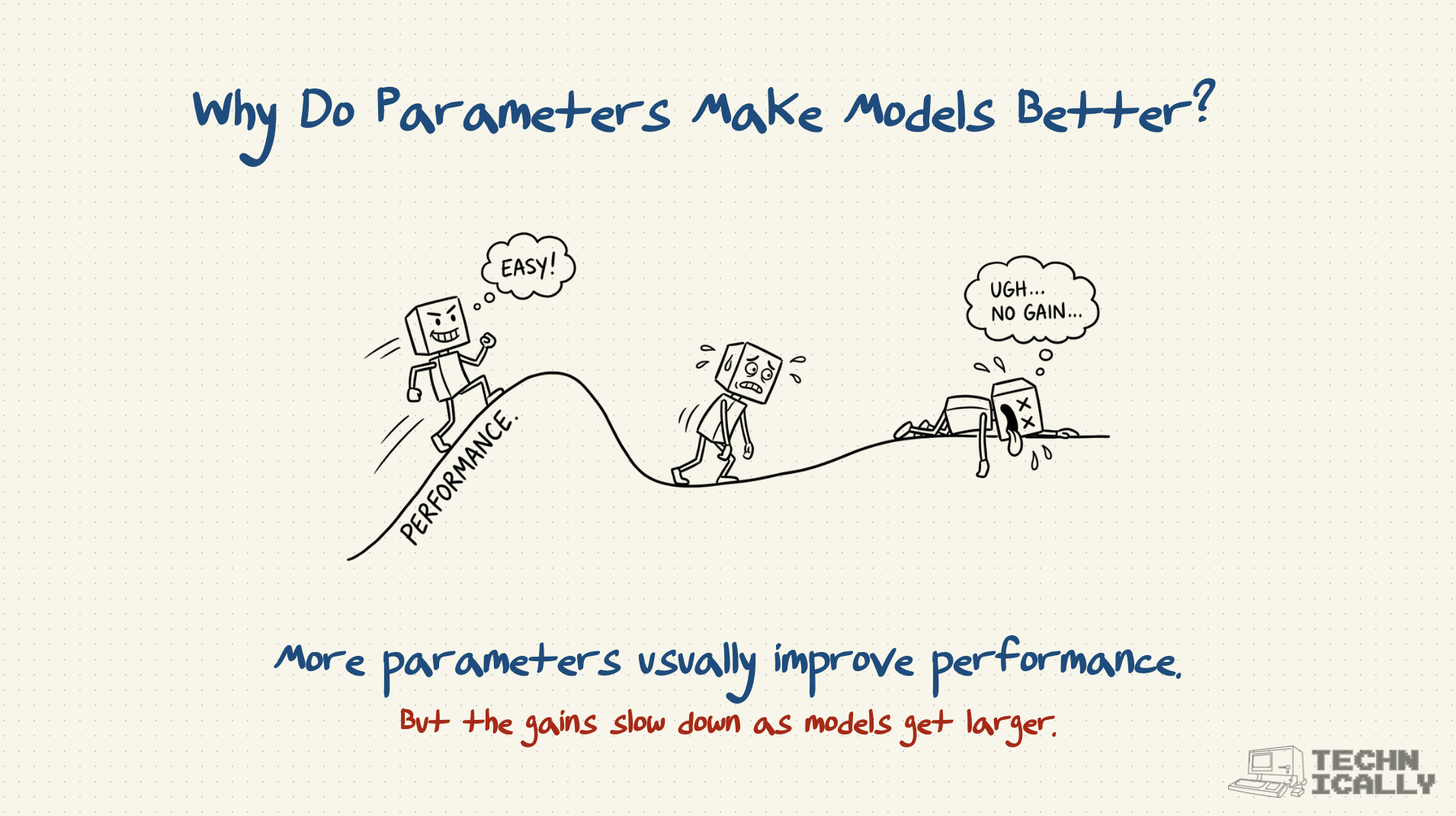
Why don't models just keep getting bigger?
Diminishing returns and practical limits. Training costs grow exponentially, and beyond a certain point, better data and training methods matter more than raw parameter count.
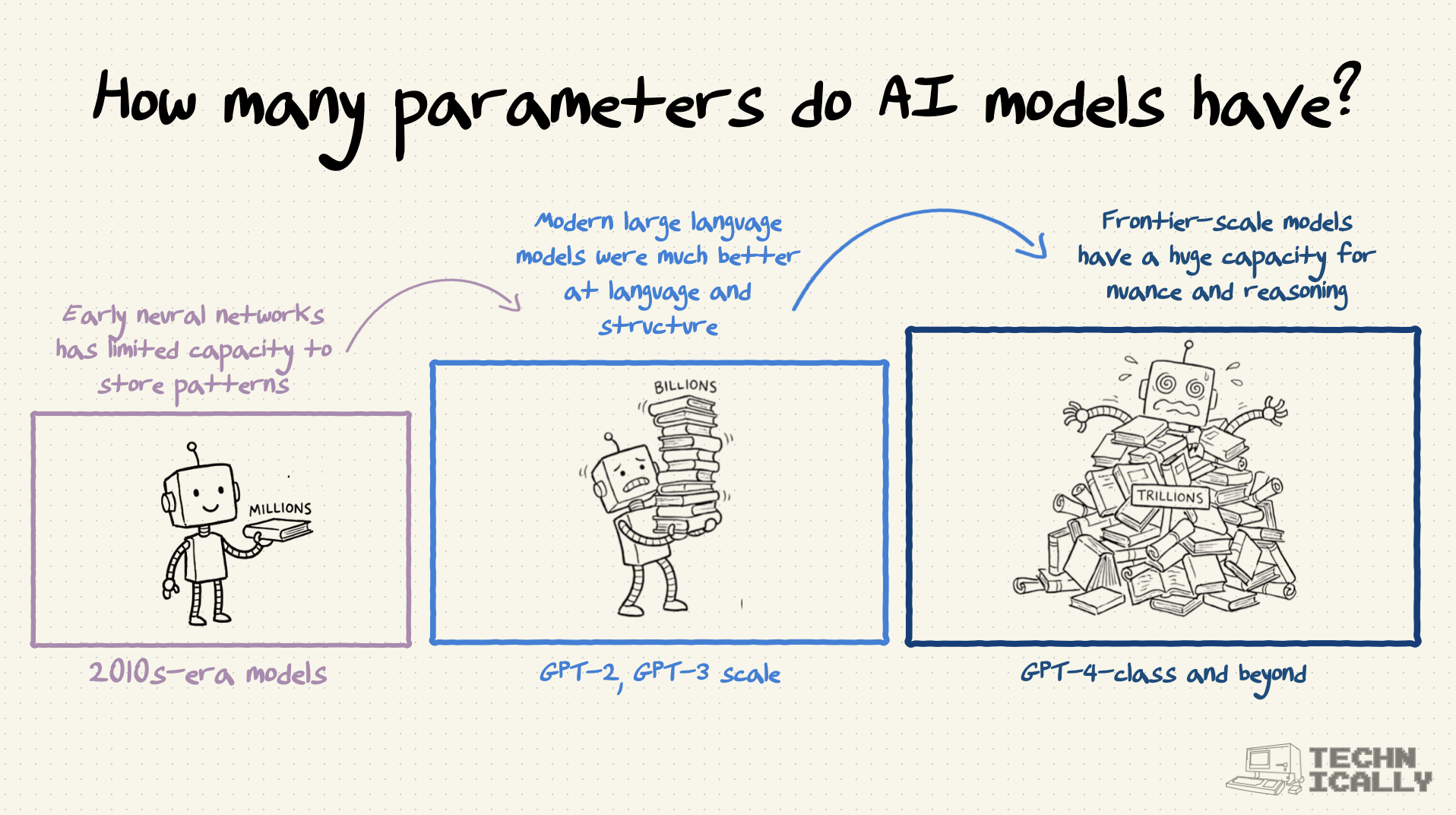
What determines how many parameters a model needs?
The complexity of the task, available training data, and computational budget. Simple tasks might need millions of parameters, while general intelligence might require trillions.