Prompt engineering is the art of talking to AI models in a way that gets you the results you actually want.
- Prompts are how you talk to GenAI models, and engineering them means making them as good as possible to get you the response you want
- The goal is to craft clear instructions and examples that guide AI toward your desired output
- Good prompts can save you money, time, and frustration when working with AI
- Think of it as learning to communicate with a very smart but literal-minded assistant
Prompt engineering is the difference between getting a rambling essay when you wanted a bullet list, and actually getting that bullet list. And if you were following the news in 2024, it was apparently “the skill to have” when it came to AI. Now, the hype has died down but good prompting is just as important.
What is prompt engineering?
Prompt engineering is essentially learning how to ask AI models the right questions in the right way. It's the practice of crafting inputs that reliably produce the outputs you're looking for, whether that's generating marketing copy, analyzing data, or answering customer questions.
Here's the thing: AI models are incredibly powerful, but they're also incredibly literal. Ask ChatGPT "write about dogs" and you might get a 500-word essay about canine evolution. Ask it "write 3 bullet points about why dogs make good pets" and you'll get exactly what you need. That difference in specificity is prompt engineering in action.
The reason prompt engineering matters is that AI models are trained to complete patterns, not read your mind. They're trying to predict what comes next based on what you've given them, so the more context and structure you provide, the better they can give you what you actually want. Remember: what’s intuitive and straightforward to you and your fellow humans is not to models. They are a specialized interface and require a specialized communication style.
How do you write good prompts?
Good prompt writing follows a few key principles that separate the pros from the people getting frustrated with AI:
Be Specific About Format
Instead of "analyze this data," try "create a 3-column table showing the top 5 trends, their impact level (high/medium/low), and recommended actions." Given a generic instruction the model will return a generic response (and is also more likely to hallucinate).
Provide Context and Role
"You are an experienced customer service manager. Help me respond to this complaint..." works better than just pasting the complaint and hoping for the best. This is often referred to as the “system prompt” but you can even just think of it as context setting for the model. Role playing…it’s not just for theater kids.
Use Examples When Possible
Show the AI what good output looks like. If you want a certain tone or style, give it an example to follow: include a blog post you like, a report that fits the format you want, etc..
Break Complex Tasks Into Steps
Models do better with specific tasks, not broader ones. Rather than asking for a complete marketing campaign, ask for customer personas first, then messaging strategy, then specific copy.
This iterative refinement applies broadly—whether you're working with coding assistants like v0 or text generation models like ChatGPT, the underlying pattern is the same: AI responds to your prompt by generating output, and small adjustments to your input can dramatically shift the result.
Start with a simple prompt, evaluate what you get, then layer in constraints and examples to refine the output.
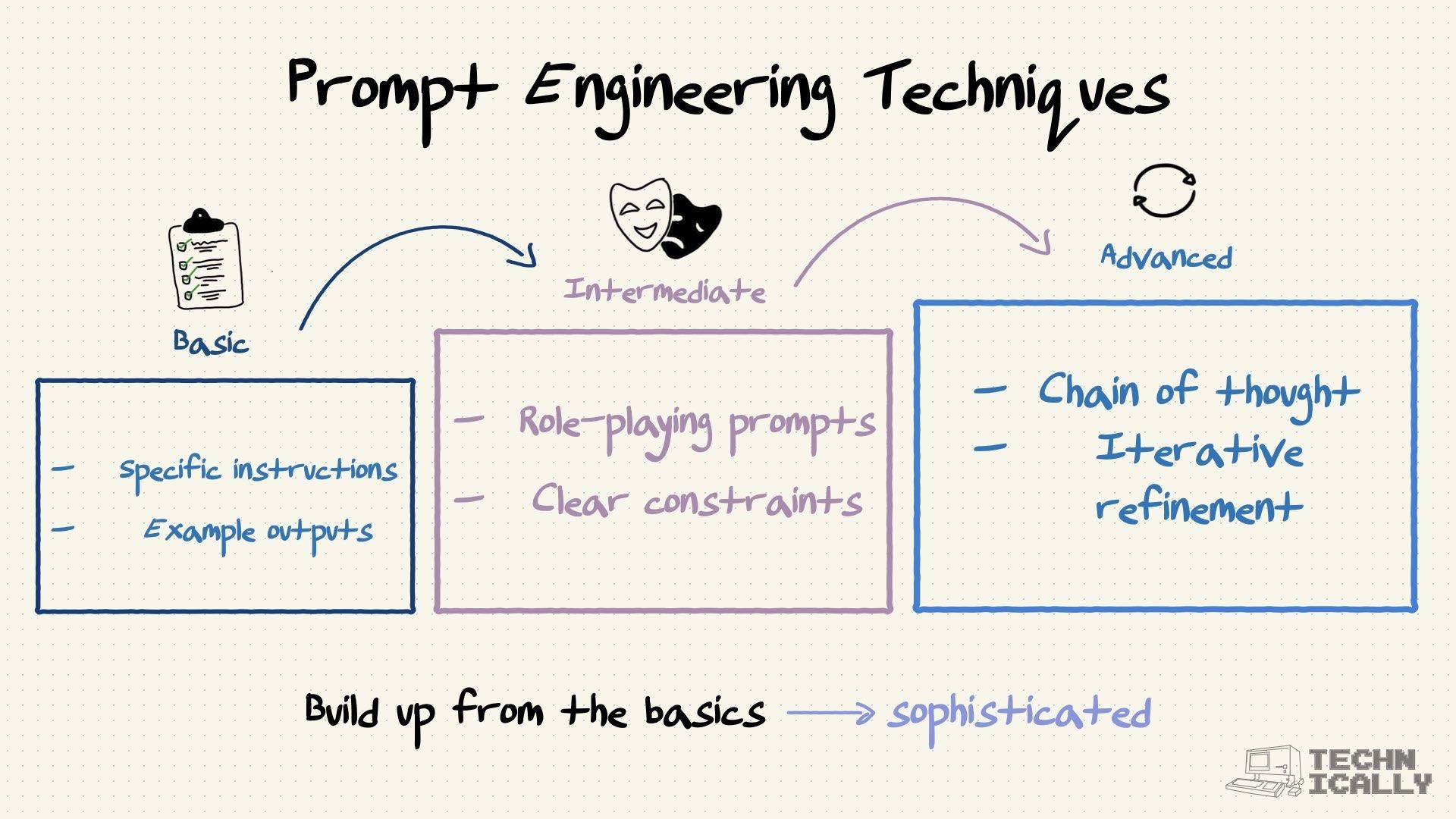
What are prompt engineering techniques?
Beyond just best practice for writing good prompts, the field has developed several reliable techniques that work across different AI models. These are more on the “engineering” side of prompt engineering.
Few-Shot Prompting
Give the AI a few examples of what you want before asking it to generate something new. Instead of just saying "write me some email subject lines," you'd show it what good ones look like first:
"Here are three email subject lines that worked well for us:
- 'Your Q3 report is ready—3 key findings inside'
- 'Quick question about tomorrow's demo'
- 'Following up: Next steps for the Henderson account'
Now write 5 more subject lines in the same style for our new product launch email."
The examples teach the model your specific style and format without you having to describe it in abstract terms.
Chain of Thought
Ask the AI to work through problems step by step rather than jumping straight to an answer. This is especially useful for anything involving logic, math, or complex reasoning.
Instead of: "What's 15% of our $847,293 annual budget?"
Try: "Let's calculate 15% of our $847,293 annual budget. Work through this step by step, showing your reasoning."
The phrase "step by step" or "let's think through this" often produces more accurate results because it forces the model to show its work rather than pattern-matching to an answer.
Constraints and Boundaries
Set clear limits on length, format, or information sources. This prevents the AI from rambling or hallucinating.
"Summarize this product spec in exactly 3 bullet points, each under 15 words" or "Only use information from the attached document—don't add anything from your training data."
Specific constraints force the model to prioritize and stay focused rather than generating everything it associates with a topic.
What are examples of good prompts?
Here are some before-and-after examples that show the difference technique makes →
Frequently Asked Questions About Prompt Engineering
Do different AI models need different prompts?
Kind of. The basic principles work everywhere—be specific, give examples, provide context. But each model has its own tendencies and response styles. Some models are naturally more verbose, so you might need to explicitly ask for brevity. Others are more conservative in their outputs, so you might need to encourage creativity or risk-taking. It's like learning to communicate with different people—same basic communication skills, but you adjust your approach based on who you're talking to.
How long should prompts be?
As long as they need to be, no longer. Some of the best prompts are one sentence. Others are several paragraphs with examples and constraints. The key is including everything the AI needs without the fluff. Think of it like giving directions—include the essential landmarks, skip the commentary about the scenery.
Can you automate prompt engineering?
To some extent. You can definitely create templates for common tasks, and some tools help optimize prompts automatically. But for complex or creative stuff, human judgment is still crucial. It's like having email templates versus writing a personal letter—automation works great for routine tasks, less so when you need finesse.
What's the difference between prompt engineering and fine-tuning?
Prompt engineering works with existing models by crafting better inputs—it's like learning to ask better questions. Fine-tuning involves actually retraining the model on additional data to change its behavior more fundamentally—more like teaching someone new skills. Prompt engineering is faster and cheaper; fine-tuning is more permanent and potentially more impactful, but requires way more resources.